PLEASE MATCH YOUR ASSIGNMENT QUESTIONS ACCORDING TO YOUR SESSION
IGNOU BCHCT-137 (January 2025 – December 2025) Assignment Questions
IGNOU BCHCT-137 (January 2024 – December 2024) Assignment Questions
PART A: COORDINATION CHEMISTRY
1. a) What is the ground state configuration of Sc+ ion? Justify.
b) Why zinc and cadmium are soft metals?
2. What is the composition of brass? Is it harder than pure copper? Give its uses.
3. Why do lanthanoids mainly show ionic bonding? What is the nature of their melting and boiling points?
4. What are the possible number of isomers for the octahedral complex ion [Co(NH3)Cl2]+?
5. What type of isomerism is exhibited in the complexes [Co(NH3)5(SO4)] Br and [Co(NH3)5Br]SO4?
6. Give the hybridized orbitals and the corresponding geometries of [Ti(H2O)6]3+ and [CoCl4]2-.
7. Explain the directional properties of the five d orbitals in a free transition metal ion with the help of suitable diagrams.
8. Give the CFSE of an octahedral complex with seven electrons in the d orbitals.
9 Give the possible electronic configurations for d3 and d6 systems in a tetrahedral crystal field.
10. Which are the cases when tetrahedral geometry is favoured over octahedral geometry for metal complexes? Why are they so?
PART B: STATES OF MATTER & CHEMICAL KINETICS
11. Calculate the i) average speed ii) root mean square speed and iii) most probable speed of oxygen molecules at 515 K. (Given Mm(O2) = 0.016 kg mol-1)
12. State the Dalton’s law of partial pressure and give its significance.
13. Explain the pressure and volume correction terms to the ideal gas equation, and deduce van der Waals equation.
14. What is meant by rate of a reaction? List and explain different types of rates used in chemical kinetics.
15. With suitable example and figure explain the integrated rate law for first order reaction.
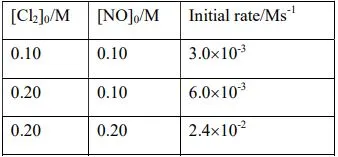
16. For the reaction, Cl2(g)+2NO(g) → 2NOCl(g), the initial concentrations, [Cl2]0 and [NO]0 are given below along the corresponding with initial rates.
Determine (i) the order of the reaction with respect to NO and Cl2; (ii) the rate law; and (iii) the rate constant
17. Give the reasons for the striking contrast in the boiling points of ethanol (351 K) and dimethyl ether (249 K). Give suitable diagrams to illustrate this.
18. What are the elements of symmetry? Give the suitable diagrams for any one of them.
19. Explain close packing in two dimensions for a crystalline solid with the help of a suitable diagram.
20. Give the consequences of Schottky and Frenkel defect.