Bought By: 12502
Rating:

Get Good Marks in your BSCG Chemistry Programme in the Term-End Exams even if you are busy in your job or profession.
We've sold over 64,209,581 Help Books and Delivered 81,022,163 Assignments Since 2002.
As our customers will tell you...yes, it really result-oriented.
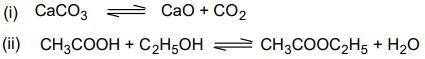 5. (a) Calculate the maximum number of phases and maximum number of degrees of freedom that
(b) Can exist for a one-component system. When is a system called invariant? Illustrate with an example.
6. Draw and explain the phase diagram of sulphur
7. (a) Define conductivity. Give its SI units.
(b) List various factors on which the conductivity of electrolytic solutions depends.
8. Draw and explain the conductometric titration curves for the titration of the following:
(i) HCl vs NaOH
(ii) CH3COOH vs NaOH
9. (a) List the functions of a salt bridge.
(b) What are the conditions which a reversible cell should satisfy.
10. (a) What is an electrolyte concentration cell? Write the expression for Ecell for such a cell.
(b) Write the reactions occurring at electrodes in the electrolysis of water. Why are a few drops of conc. H2SO4 added in this process?
PART-(B)
11. Discuss the two methods of decarboxylation of carboxylic acids and comment on the nature of products formed.
12. How can you propane the following compound starting from ethanoyl chloride?
5. (a) Calculate the maximum number of phases and maximum number of degrees of freedom that
(b) Can exist for a one-component system. When is a system called invariant? Illustrate with an example.
6. Draw and explain the phase diagram of sulphur
7. (a) Define conductivity. Give its SI units.
(b) List various factors on which the conductivity of electrolytic solutions depends.
8. Draw and explain the conductometric titration curves for the titration of the following:
(i) HCl vs NaOH
(ii) CH3COOH vs NaOH
9. (a) List the functions of a salt bridge.
(b) What are the conditions which a reversible cell should satisfy.
10. (a) What is an electrolyte concentration cell? Write the expression for Ecell for such a cell.
(b) Write the reactions occurring at electrodes in the electrolysis of water. Why are a few drops of conc. H2SO4 added in this process?
PART-(B)
11. Discuss the two methods of decarboxylation of carboxylic acids and comment on the nature of products formed.
12. How can you propane the following compound starting from ethanoyl chloride?
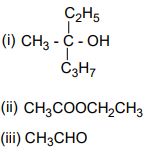 13. Briefly explain Hofmann elimination. Also give the importance of this reaction.
14. Differentiate between Sandmeyer reaction and Gattermann reaction giving suitable examples.
15. Discuss the Hinsberg test for distinguishing primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
16. (a) Discuss the preparation of 2-aminobutanoic acid using Strecker synthesis.
(b) What is cope elimination? Give reaction.
17. (a) Briefly explain this general structure and classification of peptides.
(b) What is bradykinin? Give its role?
18. How is C-terminal indentified in a peptide or a protein? Discuss.
19. (a) Explain the cyctic hemiacetal formation by glucose.
(b) Explain mutarotation in glucose.
20. Discuss the important features of structure of cellulose giving suitable diagram.
13. Briefly explain Hofmann elimination. Also give the importance of this reaction.
14. Differentiate between Sandmeyer reaction and Gattermann reaction giving suitable examples.
15. Discuss the Hinsberg test for distinguishing primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
16. (a) Discuss the preparation of 2-aminobutanoic acid using Strecker synthesis.
(b) What is cope elimination? Give reaction.
17. (a) Briefly explain this general structure and classification of peptides.
(b) What is bradykinin? Give its role?
18. How is C-terminal indentified in a peptide or a protein? Discuss.
19. (a) Explain the cyctic hemiacetal formation by glucose.
(b) Explain mutarotation in glucose.
20. Discuss the important features of structure of cellulose giving suitable diagram.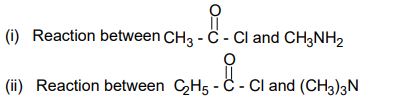 13. (a) Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
13. (a) Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
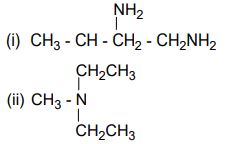 (b) Briefly explain the following reactions:
(i) Hofmann rearrangement
(ii) Schmidt rearrangement
14. (a) How will you prepare the following compounds? Give reactions.
(i) 4-methylbiphenyl
(ii) 4-hydroxyazobenzene
(iii) butter yellow dye
(b) How will you convert 4-bronobenzenmine to 4-bromobenzenol?
15. (a) Discuss the nitrosation reaction of primary amines.
(b) Discuss the nitration reaction of aniline. How would you account for the formation of different products?
16. (a) What is electrophoresis? Briefly explain. Also give its importance.
(b) What BOC-group? Which reagent is used to introduce this group?
17. How will you synthesise valine using Gabriel phthalimide synthesis?
18. Discuss the secondary structure of peptides.
19. (a) Briefly explain the phenyl osazone formation by monosaccharides.
(b) Why do D-(+)-glucose and D-(+)-mannose give the same osazone?
20. (a) What are polysaccharides? Give examples.
(b) Briefly explain the structure aspects of starch.
(b) Briefly explain the following reactions:
(i) Hofmann rearrangement
(ii) Schmidt rearrangement
14. (a) How will you prepare the following compounds? Give reactions.
(i) 4-methylbiphenyl
(ii) 4-hydroxyazobenzene
(iii) butter yellow dye
(b) How will you convert 4-bronobenzenmine to 4-bromobenzenol?
15. (a) Discuss the nitrosation reaction of primary amines.
(b) Discuss the nitration reaction of aniline. How would you account for the formation of different products?
16. (a) What is electrophoresis? Briefly explain. Also give its importance.
(b) What BOC-group? Which reagent is used to introduce this group?
17. How will you synthesise valine using Gabriel phthalimide synthesis?
18. Discuss the secondary structure of peptides.
19. (a) Briefly explain the phenyl osazone formation by monosaccharides.
(b) Why do D-(+)-glucose and D-(+)-mannose give the same osazone?
20. (a) What are polysaccharides? Give examples.
(b) Briefly explain the structure aspects of starch.To attend IGNOU BCHCT-135 Term-End Examination, you must first submit your Assignments to the university and it is possible from the BCHCT-135 study material. You can solve all necessary Assignments using Help Books. This will help in gaining good marks.
All best wishes with our efforts that you do not meet any obstacle before attending examinations next year. You can pass the BSCG Chemistry Programme Annual Exams with a good grade using Books/Materials from any one place at home or anywhere else!
ALL THE BEST!!!
Team GullyBaba