Bought By: 11113
Rating: 4.2

Get Good Marks in your B.Sc. Chemistry Programme in the Term-End Exams even if you are busy in your job or profession.
We've sold over 64,258,730 Help Books and Delivered 81,087,531 Assignments Since 2002.
As our customers will tell you...yes, it really result-oriented.
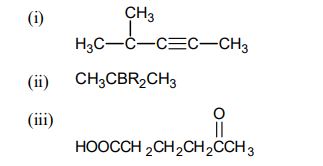 (b) Write the structure of the following compounds:
(i) Pentanedinitrile
(ii) N-ethyl-N-propylpropanamine
2. Discuss the optical activity of the following molecules giving suitable diagrams.
(i) trans-dichloroethene
(ii) meso-tartaric acid
3. Draw the conformations of 1,3-dimethylcyclohexane. Which of these conformations is more stable and why?
4. Draw the possible modes of vibrations of CH2 group present a molecule.
5. Briefly explain the guidelines/ rules to predict the relative importance of resonance structures in different molecules/species of organic compounds.
6. Define octane number. What are different factors affecting the octane number of a compound.
Give examples of additives used to increase the octane number.
7. What is Witting reactions? Give the mechanism of this reaction.
8. (a) How can you distinguish between terminal and internal alkynes using IR spectrum?
(b) How can you convert butane to 2-butyne.
9. Which position of naphthalene is more active towards electrophilic substitution? Explain giving suitable structures.
10. (a) Give any two methods of preparations of pyrrole. Also write the reactions involved.
(b) Write the resonance structures of pyridine-N-oxide.
11. Discuss the reactivity of allylic and benzylic halides in nucleophilic substitution reactions.
12. (a) How will you prepare phenol from benzene? Give the sequence of the reactions involved.
(b) Give the preparation and use of nitroglycerin.
13. Write the products of the following reactions of epoxides:
(b) Write the structure of the following compounds:
(i) Pentanedinitrile
(ii) N-ethyl-N-propylpropanamine
2. Discuss the optical activity of the following molecules giving suitable diagrams.
(i) trans-dichloroethene
(ii) meso-tartaric acid
3. Draw the conformations of 1,3-dimethylcyclohexane. Which of these conformations is more stable and why?
4. Draw the possible modes of vibrations of CH2 group present a molecule.
5. Briefly explain the guidelines/ rules to predict the relative importance of resonance structures in different molecules/species of organic compounds.
6. Define octane number. What are different factors affecting the octane number of a compound.
Give examples of additives used to increase the octane number.
7. What is Witting reactions? Give the mechanism of this reaction.
8. (a) How can you distinguish between terminal and internal alkynes using IR spectrum?
(b) How can you convert butane to 2-butyne.
9. Which position of naphthalene is more active towards electrophilic substitution? Explain giving suitable structures.
10. (a) Give any two methods of preparations of pyrrole. Also write the reactions involved.
(b) Write the resonance structures of pyridine-N-oxide.
11. Discuss the reactivity of allylic and benzylic halides in nucleophilic substitution reactions.
12. (a) How will you prepare phenol from benzene? Give the sequence of the reactions involved.
(b) Give the preparation and use of nitroglycerin.
13. Write the products of the following reactions of epoxides:
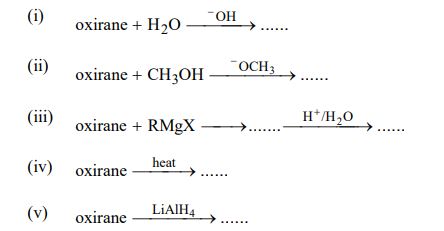 14. Write chemical reactions for the following named reactions:
(i) Etard’s reaction
(ii) Gattermann-Koch synthesis
(iii) Gattermann synthesis
(iv) Wacker process
(v) Friedel-Crafts acylation
15. Write chemical equations and reaction conditions for any five methods of preparation of carboxylic acids.
16. What is Michael addition? Explain giving suitable example and the mechanism involved.
17. Discuss the reduction of alknoyl halides using different reagents. Write the reactions involved and the products formed.
18. (i) Explain Henry reaction by giving a suitable example.
(ii) Write important uses of nitro compounds giving suitable examples.
19. How will you differentiate between primary, secondary and tertiary amines using nitrosation reaction?
20. Discuss the structure of starch giving the type of bonding and the components.
14. Write chemical reactions for the following named reactions:
(i) Etard’s reaction
(ii) Gattermann-Koch synthesis
(iii) Gattermann synthesis
(iv) Wacker process
(v) Friedel-Crafts acylation
15. Write chemical equations and reaction conditions for any five methods of preparation of carboxylic acids.
16. What is Michael addition? Explain giving suitable example and the mechanism involved.
17. Discuss the reduction of alknoyl halides using different reagents. Write the reactions involved and the products formed.
18. (i) Explain Henry reaction by giving a suitable example.
(ii) Write important uses of nitro compounds giving suitable examples.
19. How will you differentiate between primary, secondary and tertiary amines using nitrosation reaction?
20. Discuss the structure of starch giving the type of bonding and the components. (b) Explain the type of hybridisation is ethyne giving suitable diagrams.
2. (a) Draw the geometric isomers of 2,3-diiodopent-2-ene. Assign their configuration a E or Z.
(b) How can these isomers the differentiated?
3. (a) What is Walden inversion? Explain giving a suitable example.
(b) Write two more Fischer projections for the following compound:
(b) Explain the type of hybridisation is ethyne giving suitable diagrams.
2. (a) Draw the geometric isomers of 2,3-diiodopent-2-ene. Assign their configuration a E or Z.
(b) How can these isomers the differentiated?
3. (a) What is Walden inversion? Explain giving a suitable example.
(b) Write two more Fischer projections for the following compound:
 4. (a) Write the isomers of pentane. Which isomer will have the highest melting point? Explain.
(b) Which will have higher
4. (a) Write the isomers of pentane. Which isomer will have the highest melting point? Explain.
(b) Which will have higher 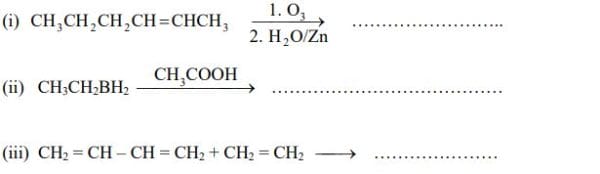 8. (a) How would you prepare a cis- and trans- alkenes from an alkyne? Give reaction for each.
(b) Which one of the following is most basic? Justify your answer.
alkanide anion; alkenide anion; alkynide anion
9. (a) Why does nitrobenzene does not undergo Friedel-Crafts alkylation?
(b) What do you understand by para-directing activators, ortho-directing activators and meta-directing deactivators?
10. (a) Give the reactions for following conversions:
(i) Furfural to furan
(ii) Pyridine to 2-hydroxypyridine
(iii) Thiophene to 2,5-dihydrothiophene
(b) Give various resonance structures of carbocation formed during electrophilic substitution of furan.
11. (a) Discuss the advantages of crown ethers in organic synthesis?
(b) Alcohols are not as strong acids as phenols, Explain.
12. Taking a suitable example for each, write the mechanism of following reactions:
i) Haloform reaction
ii) Aldol condensation
13. Explain the following reactions with the help of suitable examples:
i) E2 reaction
ii) SN 1 reaction
14. (a) How you will carry out following conversions?
8. (a) How would you prepare a cis- and trans- alkenes from an alkyne? Give reaction for each.
(b) Which one of the following is most basic? Justify your answer.
alkanide anion; alkenide anion; alkynide anion
9. (a) Why does nitrobenzene does not undergo Friedel-Crafts alkylation?
(b) What do you understand by para-directing activators, ortho-directing activators and meta-directing deactivators?
10. (a) Give the reactions for following conversions:
(i) Furfural to furan
(ii) Pyridine to 2-hydroxypyridine
(iii) Thiophene to 2,5-dihydrothiophene
(b) Give various resonance structures of carbocation formed during electrophilic substitution of furan.
11. (a) Discuss the advantages of crown ethers in organic synthesis?
(b) Alcohols are not as strong acids as phenols, Explain.
12. Taking a suitable example for each, write the mechanism of following reactions:
i) Haloform reaction
ii) Aldol condensation
13. Explain the following reactions with the help of suitable examples:
i) E2 reaction
ii) SN 1 reaction
14. (a) How you will carry out following conversions?
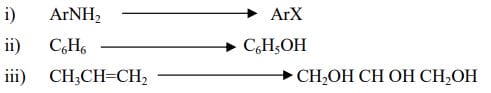
 15. Discuss the mechanism of Fischer esterification.
16. (a) How would you prepare 1, 2-benzenedicarboxylic acid by two different ways?
(b) How can the above acid be converted to its anhydride and inside? Write chemical reactions for the concessions. What is an imide group?
17. (a) What is trans-esterification? Give an example.
(b) Complete the following reactions:
15. Discuss the mechanism of Fischer esterification.
16. (a) How would you prepare 1, 2-benzenedicarboxylic acid by two different ways?
(b) How can the above acid be converted to its anhydride and inside? Write chemical reactions for the concessions. What is an imide group?
17. (a) What is trans-esterification? Give an example.
(b) Complete the following reactions:
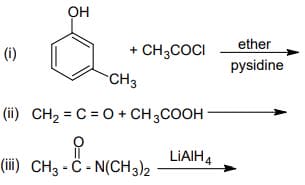 18. (a) How will you prepare 1,4-dinitrobenzene starting from benzenamine?
(b) Briefly explain the spectral characteristics of nitro compounds.
19. (a) Explain why the enantiomers of an amine cannot be separated while those of the quaternary ammonium compounds, these can be separated.
(b) What is carbylamine reaction? Explain its use.
20. Discuss Edman degradation of a peptide giving suitable reactions.
18. (a) How will you prepare 1,4-dinitrobenzene starting from benzenamine?
(b) Briefly explain the spectral characteristics of nitro compounds.
19. (a) Explain why the enantiomers of an amine cannot be separated while those of the quaternary ammonium compounds, these can be separated.
(b) What is carbylamine reaction? Explain its use.
20. Discuss Edman degradation of a peptide giving suitable reactions.To attend IGNOU CHE-05 Term-End Examination, you must first submit your Assignments to the university and it is possible from the CHE-05 study material. You can solve all necessary Assignments using Help Books. This will help in gaining good marks.
All best wishes with our efforts that you do not meet any obstacle before attending examinations next year. You can pass the B.Sc. Chemistry Programme Annual Exams with a good grade using Books/Materials from any one place at home or anywhere else!
ALL THE BEST!!!
Team GullyBaba