Bought By: 7699
Rating: 4.1

Get Good Marks in your B.Sc. Chemistry Programme in the Term-End Exams even if you are busy in your job or profession.
We've sold over 64,268,475 Help Books and Delivered 81,101,059 Assignments Since 2002.
As our customers will tell you...yes, it really result-oriented.
 9. How do the stokes, anti-stokes and Rayleigh lines appear in the Raman spectrum? Explain giving the suitable diagram.
10. Explain the IR bands exhibited by CO2 and SO2 in the light of mutual exclusion principle and arrive at the structures of these molecules.
11. Define the following terms:
(i) Auxochrome
(ii) Chromophone
(iii) Hypsochromic shift
(iv) Hypochromic effect
(v) Hyperchromic effect
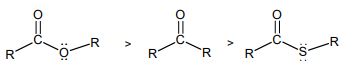
12. Discuss the effect of change of solvent from polar to non-polar on the π→π∗ and n→π∗ transitions.
13. Draw the crystal field splitting of d-orbitals of metal ions in complexes having different geometries.
14. Briefly explain fluorescence using a suitable diagram.
15. Draw the back diagram of a single beam IR spectrometer. How does a double beam instrument different from that of the single beam IR spectrometer?
16. Show that the energy difference between two spin states of a nucleus is given by
ΔE =| gN |BNBZ
17. Draw and explain the N,M,R spectrum of CH3CHO molecule.
18. Draw and explain the functioning of an ESR spectrometer.
19. What is simple cleavage? Illustrate it with the fragmentation of a suitable molecule.
20. Explain spectral signals expected in the different spectra of benzyl alcohol. What different units of the molecules are responsible for them?
9. How do the stokes, anti-stokes and Rayleigh lines appear in the Raman spectrum? Explain giving the suitable diagram.
10. Explain the IR bands exhibited by CO2 and SO2 in the light of mutual exclusion principle and arrive at the structures of these molecules.
11. Define the following terms:
(i) Auxochrome
(ii) Chromophone
(iii) Hypsochromic shift
(iv) Hypochromic effect
(v) Hyperchromic effect
12. Discuss the effect of change of solvent from polar to non-polar on the π→π∗ and n→π∗ transitions.
13. Draw the crystal field splitting of d-orbitals of metal ions in complexes having different geometries.
14. Briefly explain fluorescence using a suitable diagram.
15. Draw the back diagram of a single beam IR spectrometer. How does a double beam instrument different from that of the single beam IR spectrometer?
16. Show that the energy difference between two spin states of a nucleus is given by
ΔE =| gN |BNBZ
17. Draw and explain the N,M,R spectrum of CH3CHO molecule.
18. Draw and explain the functioning of an ESR spectrometer.
19. What is simple cleavage? Illustrate it with the fragmentation of a suitable molecule.
20. Explain spectral signals expected in the different spectra of benzyl alcohol. What different units of the molecules are responsible for them?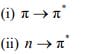 Draw a suitable diagram.
13. Explain giving a suitable diagram, the crystal field splitting of orbitals of metal ion in complexes having different geometries.
14. Explain the following terms:
(i) Vibrational relaxation
(ii) Fluorescence and phosphorescene quenching.
15. (a) Answer the following in two to three sentences:
(i) Glass container cannot be used for IR spectroscopy?
(ii) What are the basic requirements of any container which holds the sample?
(iii) What is the significance of monochromators?
(b) Draw the block diagram for the following:
(i) Raman spectrometer
(ii) IR spectrometer
16. (a) What is nuclear magneton? Calculate its value for a proton.
(b) Give two examples each for nucleic having
I = 0 and I = 1
17. Explain chemical shift. How it is expressed?
18. Discuss the esr spectrum of hydrogen atom giving a suitable diagram.
19. Discuss the mass spectrum of 2-methylpentane giving the fragments formed.
20. What would be different signals observed in the spectra of 4-ketobutanoic acid? Explain which structural units are responsible for these spectral signals.
Draw a suitable diagram.
13. Explain giving a suitable diagram, the crystal field splitting of orbitals of metal ion in complexes having different geometries.
14. Explain the following terms:
(i) Vibrational relaxation
(ii) Fluorescence and phosphorescene quenching.
15. (a) Answer the following in two to three sentences:
(i) Glass container cannot be used for IR spectroscopy?
(ii) What are the basic requirements of any container which holds the sample?
(iii) What is the significance of monochromators?
(b) Draw the block diagram for the following:
(i) Raman spectrometer
(ii) IR spectrometer
16. (a) What is nuclear magneton? Calculate its value for a proton.
(b) Give two examples each for nucleic having
I = 0 and I = 1
17. Explain chemical shift. How it is expressed?
18. Discuss the esr spectrum of hydrogen atom giving a suitable diagram.
19. Discuss the mass spectrum of 2-methylpentane giving the fragments formed.
20. What would be different signals observed in the spectra of 4-ketobutanoic acid? Explain which structural units are responsible for these spectral signals.To attend IGNOU CHE-10 Term-End Examination, you must first submit your Assignments to the university and it is possible from the CHE-10 study material. You can solve all necessary Assignments using Help Books. This will help in gaining good marks.
All best wishes with our efforts that you do not meet any obstacle before attending examinations next year. You can pass the B.Sc. Chemistry Programme Annual Exams with a good grade using Books/Materials from any one place at home or anywhere else!
ALL THE BEST!!!
Team GullyBaba