PLEASE MATCH YOUR ASSIGNMENT QUESTIONS ACCORDING TO YOUR SESSION
IGNOU MPH-07 (January 2025 – December 2025) Assignment Questions
IGNOU MPH-07 (January 2024 – December 2024) Assignment Questions
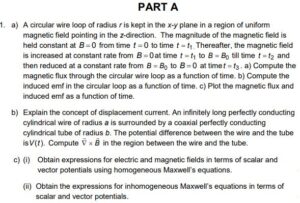
PART A
1. a) Write Maxwell’s equations in differential and integral forms. How are these equations modified in vacuum (charge and current free region)? Explain how Maxwell modified Ampere’s law and proposed generalised Ampere’s law consistent with equation of continuity and obtain the expression for the generalised Ampere’s law in differential form.
b) Derive expressions for electric and magnetic fields in terms of scalar and vector potentials using the homogeneous Maxwell’s equations. Show that the potentials associated with a given magnetic field are not unique. Express the inhomogeneous Maxwell’s equations in terms of scalar and vector potentials.
c) (i) State Lorentz force law for the motion of a charged particle in electromagnetic field.
(ii) Using this law, show that in a uniform static magnetic field, a charged particle having velocity perpendicular to the magnetic field will move on a circular path.
(iii) If the magnetic field is in the z-direction, write the x- and y-components of the equation of motion for the force law obtained in part (ii) above.
(iv) Uncouple the equations obtained in part (iii) and show that vx satisfies a harmonic oscillator equation.
2. a) Using driven harmonic oscillator model, derive an expression for AC electric susceptibility in a dielectric made of non-polar atoms/molecules.
b) Write Maxwell’s equations in dielectric material medium. Show that the homogeneous Maxwell’s equations remain unchanged for a dielectric compared to its form in vacuum.
PART B
3. a) Using Maxwell’s equations, show that electric field satisfy the three-dimensional wave equation and hence obtain an expression for the speed of the electromagnetic waves.
b) Using the boundary conditions at the interface of two dielectrics, derive the laws of reflection and refraction in geometrical optics.
c) Shown that Maxwell’s equations in electrodynamics imply the existence of a vector potential and a scalar potential which satisfy inhomogeneous wave equations in which the inhomogeneous source terms are proportional to the charge density and the current density respectively. Write the solutions of these wave equations and compare them with the expressions for scalar and vector potentials for electrostatics and magnetostatics, respectively.
4. a) Using the expressions for retarded scalar and vector potentials
Obtain the expressions for electric and magnetic fields. Show that, in the static case, these expressions reduce to Coulomb’s law and Biot-Savart law, respectively.
b) State and explain Einstein’s postulates of special theory of relativity and derive the Lorentz transformation equations.
c) (i) What is Minkowski space? Show that the invariant interval plays the role of distance in Minkowski space.
(ii) Show that the wave equation for a scalar function of the coordinates